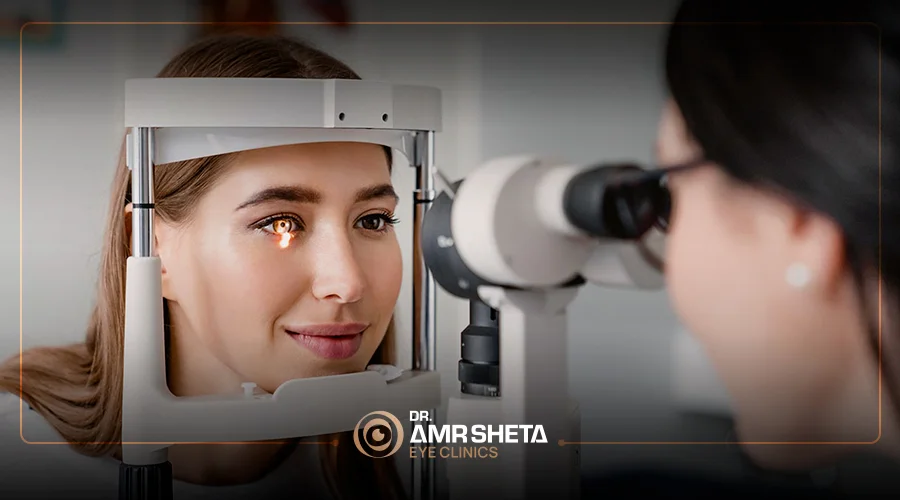
Corneal cross-linking is a relatively new procedure used to treat corneal diseases such as keratoconus, an eye condition that causes thinning of the cornea. The procedure involves applying a solution containing riboflavin (vitamin B2) to the cornea and then using ultraviolet light to strengthen the bonds between collagen fibers in the cornea.
Corneal cross-linking helps to slow or stop the progression of the disease and prevent further vision loss. It can also reduce pain, improve vision, and restore normal shape to the cornea.









115 thoughts on “Corneal cross-linking”
Al great deal for a web developer. Details: https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/var_montero
Al great deal for a web developer. Details: https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/var_montero
Al great deal for a web developer. Details: https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/var_montero
Content for your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Web Development Wizards https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Can provide a link mass to your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Your site’s position in the search results https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Free analysis of your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Content for your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Web Development Wizards https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Can provide a link mass to your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Your site’s position in the search results https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Free analysis of your website https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
SEO Optimizers Team https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
I offer mutually beneficial cooperation https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Cool website. There is a suggestion https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
I really liked your site. Do you mind https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Here’s what I can offer for the near future https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
You will definitely like it https://zetds.seychellesyoga.com/info
Content for your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Web Development Wizards https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Can provide a link mass to your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Your site’s position in the search results https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Free analysis of your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
SEO Optimizers Team https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
I offer mutually beneficial cooperation https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Cool website. There is a suggestion https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
I really liked your site. Do you mind https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Here’s what I can offer for the near future https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Content for your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Web Development Wizards https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Can provide a link mass to your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Your site’s position in the search results https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Free analysis of your website https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
SEO Optimizers Team https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
I offer mutually beneficial cooperation https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Cool website. There is a suggestion https://ztd.bardou.online/adm
Content for your website http://myngirls.online/
Web Development Wizards http://myngirls.online/
Can provide a link mass to your website http://myngirls.online/
Your site’s position in the search results http://myngirls.online/
Free analysis of your website http://myngirls.online/
SEO Optimizers Team http://myngirls.online/
I offer mutually beneficial cooperation http://myngirls.online/
Content for your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Web Development Wizards http://fertus.shop/info/
Can provide a link mass to your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Your site’s position in the search results http://fertus.shop/info/
Free analysis of your website http://fertus.shop/info/
SEO Optimizers Team http://fertus.shop/info/
I offer mutually beneficial cooperation http://fertus.shop/info/
Cool website. There is a suggestion http://fertus.shop/info/
I really liked your site. Do you mind http://fertus.shop/info/
Here’s what I can offer for the near future http://fertus.shop/info/
You will definitely like it http://fertus.shop/info/
The best prices from the best providers http://fertus.shop/info/
Additional earnings on your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Putin Carlson Interview Interview Putin. Vladimir
Putin.
Analytics of your website http://fertus.shop/info/
I would like to post an article http://fertus.shop/info/
How to contact the administrator on this issue http://fertus.shop/info/
Shall we exchange links? My website http://fertus.shop/info/
The offer is still valid. Details http://fertus.shop/info/
We offer cooperation on SEO optimization http://fertus.shop/info/
Content for your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Web Development Wizards http://fertus.shop/info/
Your site’s position in the search results http://fertus.shop/info/
Content for your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Content for your website http://fertus.shop/info/
Web Development Wizards http://fertus.shop/info/
Your site’s position in the search results http://fertus.shop/info/
SEO Optimizers Team http://fertus.shop/info/
Hi there, always i used to check webpage posts here in the early hours in the break
of day, since i like to find out more and more.
Мастерская по перетяжке мебели в Минске
обновить мебель https://obivka-divana.ru/ .
Obten tu bono casino sin deposito ahora mismo
casino online bono por registro sin deposito casino bono de bienvenida sin deposito .
Wow, fantastic weblog structure! How long have you been running
a blog for? you make blogging look easy. The entire look of your website is great, as well
as the content! You can see similar here e-commerce
of course like your website however you need to
check the spelling on quite a few of your posts.
Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very troublesome
to inform the truth then again I’ll certainly come again again.
Good site you have here.. It’s hard to find high quality writing like yours nowadays.
I seriously appreciate people like you! Take care!!
Почему рулонный газон пользуется популярностью
купить рулонный газон в москве https://rulonnyygazon177.ru/ .
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine
Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share.
Thanks! You can read similar text here: Dobry sklep
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with
SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Cheers! You can read similar art here: Najlepszy sklep
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help
with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains.
If you know of any please share. Cheers! You can read similar
text here: Sklep online
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO?
I’m trying to get my site to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good results.
If you know of any please share. Many thanks! I saw similar text here: Auto Approve List
Место, где царит уют и покой
11. Сказочный дом из бруса 9х12: мечта сбылась
дома из бруса 9х12 https://domizbrusa9x12spb.ru/ .
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to assist with SEO?
I’m trying to get my website to rank for some targeted keywords
but I’m not seeing very good success. If you know of any please share.
Appreciate it! You can read similar blog here: Backlink Building
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search
Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing
very good success. If you know of any please share. Thanks!
I saw similar art here: Backlink Building
Juegos de casino en linea en Peru para todos los gustos
mejor casino online peru online casino games peru .
Лучшие букмекеры в рейтинге
лучшие букмекерские конторы в беларуси букмекерская контора бетвиннер .
Thanks for your marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it, you may be a great author.I will remember to bookmark your blog and may
come back very soon. I want to encourage one to continue your
great work, have a nice weekend!
I have been surfing online greater than 3 hours these days, but I by no means
found any interesting article like yours. It is beautiful value sufficient for me.
Personally, if all website owners and bloggers made excellent content material
as you did, the web will be a lot more useful than ever before.
certainly like your website however you have to test the spelling on several of your
posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I
in finding it very troublesome to tell the truth however I will surely
come back again.
I have been exploring for a little for any high quality
articles or weblog posts in this sort of area .
Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website.
Reading this information So i’m glad to express that I have
an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling
I discovered just what I needed. I so much undoubtedly will make sure to do not fail to remember this website and give it a
look on a continuing basis.
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
It is not my first time to visit this website, i am browsing this
web site dailly and take fastidious facts
from here everyday.
психолог терапия w-495.ru
Saved as a favorite, I really like your website!
Whats up are using WordPress for your blog platform?
I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my
own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your
own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Wonderful post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our website.
Keep up the great writing.
Thanks for finally writing about > Corneal Cross-linking – Dr.
Amr Sheta < Liked it!
First of all I would like to say awesome blog! I had a quick
question in which I’d like to ask if you do not mind.
I was curious to know how you center yourself and clear your mind before writing.
I have had difficulty clearing my mind in getting my ideas out
there. I truly do take pleasure in writing but it just seems like the first 10 to 15
minutes tend to be wasted just trying to figure
out how to begin. Any suggestions or tips? Kudos!
I used to be able to find good information from your blog posts.
Great post.
Play and Win Real Money with Popular Games in Kenya
best online casino games kenya casino games online for real money .
Секреты выигрыша в казино
олимп казино
Онлайн казино в Беларуси: качественные игры и безопасные транзакции
онлайн казино Беларусь лучшие онлайн казино в Беларуси .
Excellent, what a webpage it is! This blog gives valuable data to
us, keep it up.
Hi, after reading this remarkable piece of writing
i am also delighted to share my experience here with colleagues.
Hi there to every one, because I am really eager
of reading this blog’s post to be updated regularly. It contains good material.
Wonderful blog! Do you have any helpful hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m completely confused ..
Any recommendations? Many thanks!
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both equally educative
and entertaining, and without a doubt, you’ve hit
the nail on the head. The issue is something not enough men and women are speaking intelligently about.
Now i’m very happy that I stumbled across this
in my search for something relating to this.
I just could not go away your website before suggesting that I really
loved the usual information a person provide
in your visitors? Is gonna be again incessantly to check out new posts
If some one wishes to be updated with hottest technologies afterward he must be
go to see this web site and be up to date every day.
whoah this weblog is wonderful i like studying your articles.
Stay up the great work! You realize, a lot of people
are looking round for this information, you could aid them greatly.
Because the admin of this web site is working, no uncertainty very rapidly it will be
well-known, due to its quality contents.
I got this website from my friend who informed me regarding this website
and now this time I am browsing this web site and reading very informative content at this time.